Our digital world brings many benefits, but it also has downsides. Research shows that too much screen time can harm our health and development. This is true for people of all ages.
Children are at a higher risk from too much device use. Studies show they might get fatter, have more behaviour problems, and lose social skills. These are just some of the dangers of technology.
But it’s not just physical health that’s at risk. Research also points to changes in our brains and mental wellbeing. Constant digital use can harm our brains. It also raises privacy concerns and can make us addicted.
This look into our connected world shows both its benefits and risks. Knowing these dangers helps us use technology more safely and wisely.
The Pervasive Nature of Digital Addiction
Today, technology is a big part of our lives. It leads to habits that are similar to addiction. Research shows that digital addiction affects the brain in the same way as substance addiction. This is because it activates the same reward centres.
This addiction is becoming more common. It’s because tech companies use clever designs to keep us hooked.
Social Media Dependency and Its Psychological Consequences
Social media makes us dependent through clever designs. It uses rewards like likes and comments to keep us coming back. This can make us less interested in real-life interactions.
Young people are often the hardest hit. Seeing perfect lives online can make them feel bad about themselves. It can also lead to emotional problems.
Studies link heavy social media use to ADHD symptoms. The fast pace of online content can make it hard to focus.
Gaming Compulsions and Their Impact on Daily Functioning
Gaming addiction is another form of digital addiction. Games are designed to keep us playing. They use rewards and social features to make us want more.
This can take over our lives. We might spend too much time playing and not enough on important things. It can affect our sleep, exercise, and responsibilities.
Games use the same tricks as slot machines to keep us playing. This makes them very addictive.
Recognising Problematic Behaviour Patterns in Mobile Gaming
Mobile gaming is addictive because it’s always available. Signs of addiction include:
- Thinking about gaming all the time
- Feeling bad when you can’t play
- Spending more time playing to feel good
- Trying but failing to control gaming
- Not caring about other hobbies anymore
These signs show when gaming becomes an addiction. Mobile devices make it easy to play anywhere, anytime.
TikTok’s Algorithmic Design and Addictive Features
TikTok uses its algorithm to keep you hooked. It knows what you like and shows you more. This makes it hard to stop watching.
It has features that make it addictive:
- It rewards you with new content
- It shows you videos without asking
- It uses likes and shares to make you feel good
- It shows you content that you like, making you feel like you’re part of a group
These features make TikTok very addictive. It’s even more addictive for young people whose brains are more open to these tricks.
What Are the Negatives of Technology on Mental Wellbeing
Digital innovations bring many benefits, but they also have downsides. The constant need to stay connected affects our mental health and sleep.

Anxiety and Depression Linked to Social Media Comparison
Social media makes it easy to compare ourselves to others. We see perfect lives that aren’t real. This can make us feel bad about ourselves.
Studies show that seeing perfect lives online can lower our self-esteem. Teenagers are often the hardest hit, feeling like they don’t measure up.
Brain scans show how social media affects our emotions. The need for likes and comments can be addictive. It changes our brain in ways similar to addiction.
This can make us feel lonely, even when we’re connected online. We might feel:
- Not good enough
- Worried about what others think
- Down because we don’t compare well
Screen Time Correlation With Sleep Quality Disorders
Using devices at night messes with our sleep. Studies show that screen time before bed hurts our sleep.
It’s not just the light. The fun stuff on screens keeps our minds busy when we should be sleeping.
Blue Light Emission From Apple iPhone and Samsung Devices
Smartphones give off blue light that messes with our sleep hormone. Apple and Samsung devices have bright screens that make it hard to sleep.
Using blue light filters or night mode can help. They cut down on blue light at night. But they don’t solve all sleep problems.
Notification Systems and Their Impact on Stress Levels
Alerts all the time make it hard to relax. We stay on edge, even when we’re supposed to be resting.
This can raise our stress hormones and hurt our sleep. Many people wake up during the night to check their phones.
To keep our minds healthy, we can change how we handle notifications. Here are some tips:
- Set times when you won’t be disturbed
- Turn off unnecessary alerts
- Make your bedroom a phone-free zone
Privacy Erosion in Contemporary Digital Environments
Digital platforms have opened up new ways to connect and access information. But, this convenience comes at a high cost to our privacy. The loss of digital privacy is a major concern with technology.
Data Collection Practices of Major Technology Corporations
Big tech companies use advanced tracking methods to collect a lot of personal info. They do this often without telling users or getting their consent.
They collect data in many ways:
- Cookies and tracking pixels
- Location services
- Behavioural monitoring
- Cross-device synchronisation
This data collection builds detailed profiles of users. Companies use this info for targeted ads and to make services more personal.
Surveillance Capitalism and Personal Information Exploitation
Surveillance capitalism is an economic model that sees personal data as valuable. It constantly monitors and analyses user behaviour for profit.
This system turns private moments into data for sale. Companies sell this data to advertisers and others.
This changes how companies see their users. People are seen as products, not customers, in this data-driven world.
Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica Data Harvesting Incident
The Cambridge Analytica scandal showed how personal data can be used for politics. It involved taking data from millions of users without their consent.
This data was used to make psychological profiles for political ads. It showed how privacy erosion can affect democracy.
Google’s Advertising Tracking Across Multiple Platforms
Google tracks users across its services and partner sites. It builds detailed profiles using search history, location, and email content.
This tracking allows for very targeted ads. It shows how surveillance capitalism works on a large scale.
These actions threaten our freedom and digital rights. They show we need stronger privacy laws in our connected world.
Cybersecurity Threats and Personal Digital Vulnerabilities
Our society’s reliance on technology has led to a rise in cybersecurity threats. Digital systems are now part of our daily lives and critical infrastructure. This has created many vulnerabilities that can harm personal security and institutions.
These threats use both technical weaknesses and human psychology. Cybercriminals keep finding new ways to get past security. This can cause financial loss and disrupt essential services.

Ransomware Attacks Targeting Healthcare and Educational Institutions
Ransomware attacks are a big problem for critical sectors. Hospitals face serious issues when patient data is encrypted. Schools also suffer, with learning and research being disrupted.
These attacks start with phishing emails. Once clicked, the malware encrypts files and demands payment. Attackers threaten to leak sensitive data if they don’t get paid.
Hospitals have had to delay treatments and cancel surgeries. Schools have lost valuable data. The costs go beyond the ransom, including recovery and fines.
Identity Theft Through Sophisticated Phishing Techniques
Identity theft is a big worry. Phishing has become more advanced. Scammers now make fake websites and emails that look real.
They use stolen data to make their emails seem genuine. These emails might talk about recent purchases or account activity. They try to create a sense of urgency.
Being a victim of identity theft can lead to financial disaster. It can also cause emotional distress. The damage can last for years.
Common Social Engineering Tactics Employed by Cybercriminals
Social engineering uses tricks to get information. Scammers might pretend to be someone else or offer something in return for your details. They also try to follow people into restricted areas.
They use various tactics to trick people. They study their targets online before making their move. This makes their tricks seem real.
Password Security Best Practices for Personal Protection
Strong passwords are key to protecting yourself. Longer passwords are better than complex ones. Using passphrases is even safer.
Adding extra security steps, like multi-factor authentication, is a good idea. This means you need something you know and something you have. Biometric verification is the most secure.
Password managers can help keep your passwords safe. They make sure each one is unique. Changing your passwords regularly is also important.
| Security Method | Implementation Difficulty | Protection Level | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Manager | Easy | High | Continuous |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Medium | Very High | Always enabled |
| Password Changes | Easy | Medium | Every 3-6 months |
| Passphrases | Medium | High | For new accounts |
Good digital hygiene can help avoid identity theft. Learning about social engineering can help spot scams. Reporting any suspicious activity quickly can prevent harm.
The Transformation of Social Relationships and Communication
Digital technology has made us more connected but also more alone. This section looks at how social relationships change with digital communication. Sometimes, these changes are not what we expect.
Diminished Quality in Face-to-Face Interaction
Screens take up most of our time, making us less skilled in face-to-face talks. We spend less time learning to read facial expressions and body language.
Studies show that cutting down on tech use boosts emotional intelligence. But, the art of real conversations is lost when we turn to digital ones instead.
Social Isolation Despite Digital Hyper-Connectivity
Many feel social isolation even though they’re always online. This is because we’re replacing deep talks with shallow digital chats.
Research links social media to feeling isolated. Brain scans show how missing out on face-to-face talks affects our social skills.
WhatsApp and Messenger’s Effect on Conversation Depth
Instant messaging apps focus on quick messages, not deep talks. Our chats become short and broken, not long, meaningful conversations.
The endless stream of notifications messes with how we talk and listen. It changes how we share and connect with others.
Digital Communication Versus Emotional Connection Quality
Text-based digital communication can’t match the emotional depth of real talks. The subtleties of tone, timing, and presence are lost in digital chats.
This can cause misunderstandings and emotional distance. While digital messaging is handy, it sacrifices the quality of our social relationships.
Economic Disruption and Employment Market Challenges
Technology is changing the economy, bringing both chances and big challenges for jobs. This economic disruption comes from two main areas: automation taking over old jobs and the growth of the gig economy. We need to look closely at how these changes affect job security and worker well-being.

Automation’s Impact on Traditional Manufacturing and Service Jobs
Automation is taking over tasks that humans used to do. Artificial intelligence and robots are now doing things like making things, checking quality, and making big decisions.
In service industries, things are changing too. Automated kiosks are replacing cashiers, and AI chatbots are answering customer service calls. This means old jobs are disappearing faster than new ones are being created.
People often can’t get the training they need for new tech jobs. The European Parliament’s research shows that automation is hitting mid-skilled jobs hard, leading to a split in the job market.
The Precarious Nature of Platform-Based Gig Economy Work
Digital platforms offer flexible work but lack stability. Gig economy workers are seen as independent contractors, not employees.
This means they miss out on benefits like health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans. They also face unpredictable income without set hours or a minimum wage.
Uber’s Business Model and Driver Compensation Structures
Uber shows how gig economy models shift risks to workers. Drivers pay for their cars, fuel, and upkeep but get variable pay.
After paying for these costs, many drivers earn less than the minimum wage. The company’s pricing system also controls how much they make, without asking drivers.
Deliveroo’s Impact on Restaurant Workers’ Employment Conditions
Deliveroo and similar platforms are changing how restaurants hire workers. Many places are cutting permanent staff and using platform workers during busy times.
This change means less stable work for traditional staff and tough conditions for platform riders. The focus is on flexibility, not job security.
Digital Divide and Technological Access Inequality
Today, having access to digital tools is key to getting ahead. But, not everyone has the same chance. This gap in technology access leads to unfair disadvantages in many areas.

Socioeconomic Disparities in Technology Access and Literacy
How much money you have affects your access to technology. Richer families often have more devices and keep up with the latest tech.
Poorer families have to choose between basic needs and digital tools. This makes it hard for them to learn about technology.
Those who don’t use technology often find it hard to get jobs or take part in society. This is because they lack the skills needed for today’s world.
Tools to control and monitor online activity assume families have access to technology. But, many families can’t afford this, making it hard for them to use the internet safely.
Educational Disadvantages in Underserved Community Settings
Schools in poor areas often don’t have the tech that wealthier schools do. This makes it hard for students to learn from the start.
Students without internet or modern devices can’t do online homework. They miss out on learning tech skills that others get easily.
Remote Learning Technology Gaps During COVID-19 Pandemic
The pandemic showed how big the tech gap is in schools. Many students in poor areas didn’t have devices or internet for online learning.
Some schools said 20-30% of students didn’t have internet at home. This meant they lost out on learning that could take years to catch up on.
Teachers found it hard to teach online because students had different tech levels. This shows that fixing the tech gap is key to fair education.
Broadband Access Disparities Between Urban and Rural Areas
Most money for internet goes to cities because they have more people. Rural areas have fewer options and pay more for slower internet.
About 30% of rural Americans don’t have fast enough internet. This makes it hard for them to join in with modern life.
The lack of fast internet affects learning, health care, jobs, and being part of society. Without help, these areas might get left behind in the digital world.
Environmental Costs of Rapid Technological Advancement
Technology’s impact on the environment is huge, but often hidden from us. The making, using, and throwing away of devices harm our planet. This cycle uses up a lot of resources.
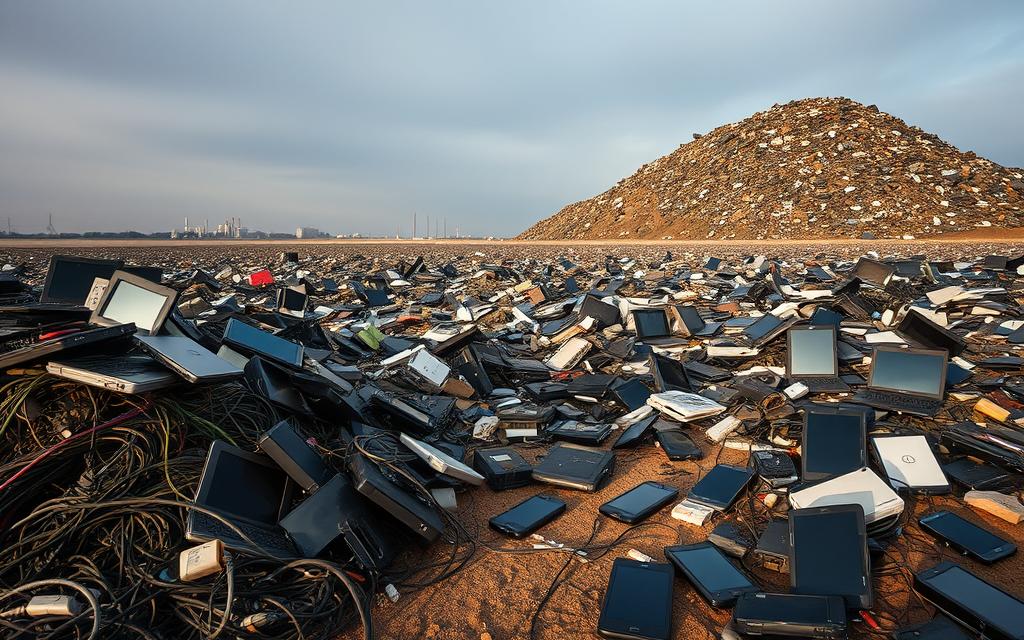

Electronic Waste Generation and Responsible Disposal Challenges
Fast technology changes lead to a lot of electronic waste worldwide. People often get rid of devices before they’re worn out. This creates a big problem.
Recycling electronics is hard because they contain harmful materials. These can pollute soil and water if not disposed of right.
Many countries struggle with this waste. They get old technology from other places. This is bad for the environment and raises big questions.
Energy Consumption of Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud computing uses a lot of energy, but we don’t see it. Data centres run all the time, using as much power as a small city.
These centres need a lot of power for their servers and cooling. This puts a lot of strain on the power grid and adds to pollution.
Amazon Web Services Data Centre Energy Requirements
Amazon Web Services has a huge cloud network. Their data centres use a lot of electricity to keep everything running.
Despite efforts to be more efficient, AWS’s energy use is big. They use new cooling tech and invest in green energy.
Microsoft Azure’s Carbon Footprint and Sustainability Initiatives
Microsoft Azure is working hard to reduce its environmental impact. They aim to be carbon negative by 2030.
They’re doing many things to help the planet. This includes:
- Using 100% renewable energy for data centres
- Using new water cooling systems
- Working on carbon capture and storage
These steps are important for reducing the tech sector’s harm to the environment.
| Environmental Factor | Current Impact | Industry Response | Future Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic Waste Volume | 53.6 million metric tonnes (2019) | Extended producer responsibility programmes | Developing circular economy models |
| Data Centre Energy Use | 1% of global electricity demand | Renewable energy procurement | Meeting growing computational demands |
| Carbon Emissions | 2.3% of global emissions | Carbon neutrality commitments | Scope 3 emissions reduction |
| Water Consumption | Significant cooling requirements | Water-efficient cooling systems | Drought region operations |
The tech sector is working on these big environmental issues. But, it needs to keep improving. Making tech more sustainable is key to its growth.
Cognitive Development Concerns in Technology-Reliant Societies
Our growing use of digital tech is changing how we think and remember. The endless flow of info and quick access to knowledge are reshaping our minds.
Attention Span Reduction and Multitasking Effectiveness
Studies show our attention span has dropped from 12 to 8 seconds in 20 years. This change is linked to more screen time and digital use.
Many think using tech makes them more efficient. But science says multitasking can cut cognitive performance by up to 40%.
Functional MRI scans show heavy internet users’ brains work differently. They have less activity in areas for deep thinking and focus.
Memory Function Changes in Google-Dependent Cultures
Our memory habits have changed a lot with digital tech. Now, we often remember where to find info, not the info itself.
The Google Effect on Information Retention and Recall
Psychologists call this the “Google effect.” Knowing we can find info later makes us less likely to remember it. This changes how we learn and remember.
One study found people who thought info would be saved digitally remembered less. Just thinking we can find it later affects our memory.
Digital Navigation Versus Spatial Memory Development
GPS has changed how we navigate, but it might harm our brains. Traditional navigation boosts our spatial memory and problem-solving skills.
Using GPS instead of mental maps can harm hippocampal development. This area is key for memory and spatial awareness.
London taxi drivers, who memorise streets, have bigger hippocampi. With GPS, we miss out on these brain exercises that improve our memory.
Studies on limiting tech use show big cognitive gains. People do better at reading emotions, understanding social cues, and remembering things after cutting down on screens.
Conclusion
Technology has two sides. It brings great benefits but also risks if not used wisely. Finding the right balance is key.
Studies show that good digital habits can boost our wellbeing. The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests limits on screen time for kids. It’s important to set boundaries, enjoy offline time, and use parental controls.
Workplaces and laws need to tackle digital overload and privacy issues. Research shows that technology can improve our mental health and social lives if used correctly. True digital wellbeing comes from using technology in a way that respects our humanity.
FAQ
What are the main negative impacts of technology on physical and mental health?
Too much tech use can lead to obesity, bad behaviour, and poor social skills. It also causes digital addiction, anxiety, depression, and sleep problems from too much screen time.
How does digital addiction develop, and which platforms are most concerning?
Digital addiction comes from tech designs that play on our psychology. For example, TikTok’s endless scroll and mobile games’ rewards can make us use tech too much. This can harm our daily lives and feel like ADHD symptoms.
In what ways does technology contribute to mental health issues like anxiety and low self-esteem?
Social media makes us compare ourselves to perfect online images, which can hurt our self-esteem and cause anxiety, mainly in teens. Devices like iPhones and Samsungs also mess with our sleep and stress levels.
What privacy risks do major technology companies pose to users?
Big tech like Facebook and Google collect a lot of our data without always asking. The Cambridge Analytica scandal shows how our info can be used badly, hurting our privacy and freedom online.
How significant are cybersecurity threats in today’s technology-dependent society?
Cyber threats are getting worse, with attacks on places like hospitals and schools. Phishing scams can steal our identities. To stay safe, use strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
Does technology improve or harm the quality of social relationships?
Tech can make it easy to stay in touch but often makes our connections shallower. Relying too much on apps like WhatsApp can lead to feeling lonely, misunderstandings, and less emotional intelligence.
What are the economic downsides of technological advancement?
New tech can replace jobs, and the gig economy, seen in Uber and Deliveroo, offers unstable work with little security or fair pay.
How does the digital divide exacerbate social inequality?
Not everyone has equal access to tech, which widens the gap between rich and poor. This is a big problem in education, where some students can’t keep up because of lack of resources and internet.
What environmental impacts are associated with technology?
Tech is bad for the planet, causing e-waste, using lots of energy, and producing carbon emissions. For example, data centres like Amazon’s use as much power as a small city, and throwing away old tech is harmful.
How does technology affect cognitive development and brain function?
Too much tech can make our brains less focused, hurt our memory, and change how our brains develop. Studies show that cutting down on screen time can help our brains work better and help us understand people better.
Can the negative effects of technology be mitigated?
Yes, by using tech wisely, setting limits, and teaching kids to control their screen time. It’s also important to have offline time and connect with people face-to-face for our well-being.